papers
2024
-
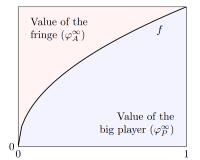 The value of being indispensable: A cooperative approach to bargaining with a continuum of playersMartin Stancsics2024
The value of being indispensable: A cooperative approach to bargaining with a continuum of playersMartin Stancsics2024This paper investigates the idea of using random order values, a concept from cooperative game theory, to model bargaining outcomes in games with one indispensable player and a continuum of fringe players. Two important special cases of random order values are discussed in detail: the Shapley value and the weighted value. I show that this approach proves to be very tractable, and leads to results that are in line with one’s intuitive expectations about bargaining outcomes. Thus, it can be a useful tool in modelling situations where one does not want to attribute all the bargaining power to one side of the market, and at the same time would like to avoid having to deal with an explicit multi-stage bargaining game. The utility of this approach is demonstrated via a simple model of a two-sided market.
@unpublished{stancsics2024value, author = {Stancsics, Martin}, title = {The value of being indispensable: A cooperative approach to bargaining with a continuum of players}, year = {2024}, } -
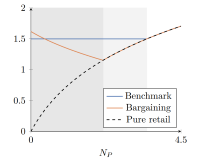 Hybrid platforms and bargaining powerMartin Stancsics2024
Hybrid platforms and bargaining powerMartin Stancsics2024This paper explores the effects of a platform selling their own products in addition to acting as intermediaries (hybrid platform) in a setting when bargaining takes place between the platform and the potential entrants. It highlights a so-far underappreciated aspect of hybrid platforms: having their own products increases their bargaining power over the other sellers. This change in bargaining might lead to lower entry, and thus reduced product variety which in turn can have negative welfare consequences for the consumers. The results and methods described in this paper are also applicable to other similar settings, such as vertical integration with a monopolistic upstream supplier.
@unpublished{stancsics2024hybrid, author = {Stancsics, Martin}, title = {Hybrid platforms and bargaining power}, year = {2024}, } -
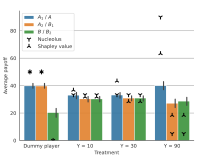 Characterizing Multiplayer Free-Form Bargaining: A Lab experimentMia Lu, and Martin Stancsics2024
Characterizing Multiplayer Free-Form Bargaining: A Lab experimentMia Lu, and Martin Stancsics2024This experiment investigates coalition-formation and surplus division between three players in a free-form bargaining environment. We find that players’ payoffs are increasing in their bargaining power, but only when forming a smaller coalition and excluding one of the non-monopolist players is a credible threat. This is qualitatively consistent with the theoretical predictions of the nucleolus from cooperative game theory, but the observed payoff inequality is significantly lower than the theoretical predictions. Our results highlight that fairness considerations seem to play an important role even under free-form bargaining: equal splits make up a large fraction of the outcomes, and fairness-related arguments are used frequently during bargaining. We also find considerable heterogeneity between players both in terms of bargaining behavior and stated preferences.
@unpublished{lu2024characterizing, author = {Lu, Mia and Stancsics, Martin}, title = {Characterizing Multiplayer Free-Form Bargaining: A Lab experiment}, year = {2024}, }
2021
-
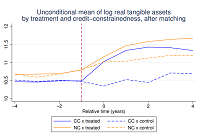 Credit constrained firms and government subsidies: evidence from a European Union programEszter Balogh, Adám Banai, Tirupam Goel, and 4 more authors2021
Credit constrained firms and government subsidies: evidence from a European Union programEszter Balogh, Adám Banai, Tirupam Goel, and 4 more authors2021We assess the effects of non-repayable subsidies on financially constrained and unconstrained Hungarian SMEs. Using rejected subsidy applicants as control group and bank queries to the credit-registry to identify firms that applied for but did not receive a loan, we show that subsidies generate a sizeable incremental impact on asset growth of constrained firms relative to unconstrained businesses. This effect, however, is transitory and does not translate into higher sales, profitability or productivity. Financing, therefore, may not be the primary hurdle for these SMEs, and credit constraints may reflect other shortcomings, such as lack of good management or viable projects.
@techreport{balogh2021credit, title = {Credit constrained firms and government subsidies: evidence from a European Union program}, author = {Balogh, Eszter and Banai, Ad{\'a}m and Goel, Tirupam and Lang, P{\'e}ter and Stancsics, Martin and Tak{\'a}ts, El{\H{o}}d and Telegdy, {\'A}lmos}, institution = {BIS Working Papers}, year = {2021}, }
2020
-
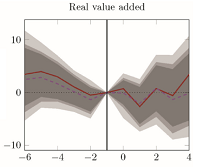 Waste of money or growth opportunity: The causal effect of EU subsidies on Hungarian SMEsÁdám Banai, Peter Lang, Gabor Nagy, and 1 more authorEconomic Systems 2020
Waste of money or growth opportunity: The causal effect of EU subsidies on Hungarian SMEsÁdám Banai, Peter Lang, Gabor Nagy, and 1 more authorEconomic Systems 2020Although EU subsidies aiming at economic development play a pivotal role not only for Hungary but for the entire European Union as well, there is a debate regarding their effectiveness in the literature. This paper investigates the impact of direct economic development subsidies extended in the context of Structural Funds and the Cohesion Fund as part of the 2007–2013 programming period of the European Union on Hungarian micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. Based on a micro database, we evaluate the impact of corporates’ first subsidies on various performance indicators, using a combination of propensity score matching and fixed effects panel regression. According to our results, economic development funds had a significant positive effect on the number of employees, sales revenue, gross value added and, in some cases, operating profit. However, the labour productivity of enterprises was not significantly affected by any of the support schemes. Furthermore, by explicitly comparing non-refundable subsidies (grants) and refundable assistance (financial instruments), we find that there is no significant difference in the effectiveness of the two types of subsidy.
@article{banai2020waste, title = {Waste of money or growth opportunity: The causal effect of EU subsidies on Hungarian SMEs}, author = {Banai, {\'A}d{\'a}m and Lang, Peter and Nagy, Gabor and Stancsics, Martin}, journal = {Economic Systems}, volume = {44}, number = {1}, pages = {100742}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Elsevier}, } -
 Unfolding the hidden structure of the Hungarian multi-layer firm networkAndras Borsos, and Martin Stancsics2020
Unfolding the hidden structure of the Hungarian multi-layer firm networkAndras Borsos, and Martin Stancsics2020In this paper we offer an explorative, mainly descriptive analysis about the multi-layered network of Hungarian firms. To conduct this study, we obtained access to firm-level supplier information, on which we could superimpose also the ownership background of all Hungarian companies. Our primary focus was to explore the topological origins of shock propagation phenomena among firms. As both the supplier and the ownership layers are considered to be among the most significant shock-transmitting mediums, our data is ideal to gain insight into previously unobserved structural drivers of spreading processes. We found (i) several topological traits on micro-, meso-, and macro-scale as well, which can be responsible for facilitating contagious processes via supplier links; (ii) we could also identify separated blocks of the economy (representing different production chains) within which shocks can more freely spread in the system; (iii) furthermore, we could assess the significance of economic entities regarding the extent they can influence the economy via their ownership relations.
@techreport{borsos2020unfolding, title = {Unfolding the hidden structure of the Hungarian multi-layer firm network}, author = {Borsos, Andras and Stancsics, Martin}, year = {2020}, institution = {MNB Occasional Papers}, }
2017
-
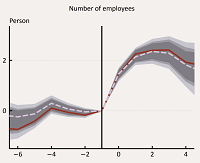 Impact evaluation of EU subsidies for economic development on the Hungarian SME sectorÁdám Banai, Péter Lang, Gábor Nagy, and 1 more author2017
Impact evaluation of EU subsidies for economic development on the Hungarian SME sectorÁdám Banai, Péter Lang, Gábor Nagy, and 1 more author2017Although EU funds play a pivotal role not only for Hungary but for the entire European Union as well, there is debate regarding their effectiveness in the literature. This paper investigates the impact of direct economic development subsidies extended in the context of the Cohesion Policy programmes as part of the 2007-2013 programming period of the European Union, on Hungarian micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. Based on a micro database, we assess the effects of the beneficiaries’ first subsidies on various performance indicators, using a combination of propensity score matching and fixed effects panel regression. According to our results, economic development funds had a significant positive impact on the number of employees, sales revenue, gross value added and in some cases, operating profit. However, the labour productivity of beneficiaries was not significantly affected by any of the support schemes. Furthermore, by explicitly comparing non-refundable subsidies (grants) and refundable assistance (financial instruments) extended under the Structural Funds and the Cohesion Fund, we find that there is no significant difference in their effectiveness.
@techreport{banai2017impact, title = {Impact evaluation of EU subsidies for economic development on the Hungarian SME sector}, author = {Banai, {\'A}d{\'a}m and Lang, P{\'e}ter and Nagy, G{\'a}bor and Stancsics, Martin}, year = {2017}, institution = {MNB Working Papers}, } -
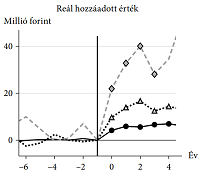 A gazdaságfejlesztési célú EU-támogatások hatásvizsgálata a magyar kkv-szektorraÁdám Banai, Péter Lang, Gábor Nagy, and 1 more authorKözgazdasági szemle 2017
A gazdaságfejlesztési célú EU-támogatások hatásvizsgálata a magyar kkv-szektorraÁdám Banai, Péter Lang, Gábor Nagy, and 1 more authorKözgazdasági szemle 2017A gazdaságfejlesztési célú európai uniós támogatások nemcsak Magyarország, de az Európai Unió számára is kiemelten fontosak, hatásosságuk azonban a szakirodalomban vita tárgya. Tanulmányunkban a Strukturális Alapok és a Kohéziós Alap 2007–2013-as európai uniós költségvetési ciklushoz tartozó, közvetlen gazdaságfejlesztési célú támogatásainak hatását vizsgáljuk a magyar mikro-, kis- és középvállalati szektorra. Mikroadatbázisra épülő hatásvizsgálatunkban a becsült részvételi valószínűségen (propensity score) alapuló párosítás és fixhatás-panelregresszió kombinációját alkalmazva értékeltük a támogatások hatását. Eredményeink szerint a gazdaságfejlesztési célú források szignifikáns pozitív hatást gyakoroltak a foglalkoztatotti létszámra, az árbevételre, a bruttó hozzáadott értékre, valamint egyes esetekben az üzemi eredményre is. A vállalkozások munkatermelékenységét azonban egyik vizsgált támogatási forma sem befolyásolta szignifikánsan.* Journal of Economic Literature (JEL) kód: D04, G38, H25, O22.
@article{banai2017gazdasagfejlesztesi, title = {A gazdas{\'a}gfejleszt{\'e}si c{\'e}l{\'u} EU-t{\'a}mogat{\'a}sok hat{\'a}svizsg{\'a}lata a magyar kkv-szektorra}, author = {Banai, {\'A}d{\'a}m and Lang, P{\'e}ter and Nagy, G{\'a}bor and Stancsics, Martin}, journal = {K{\"o}zgazdas{\'a}gi szemle}, volume = {64}, number = {10}, pages = {997--1029}, year = {2017}, publisher = {Magyar Tudom{\'a}nyos Akad{\'e}mia}, }
2016
-
 Interest Rates and Asset Distributions of Naive Hyperbolic DiscountersMartin Stancsics2016
Interest Rates and Asset Distributions of Naive Hyperbolic DiscountersMartin Stancsics2016This thesis extends the heterogeneous agent incomplete market model of Huggett (1993) with partially naive hyperbolic discounting. An Euler-equation is derived for the agents with this discounting model. Possible pathologies of this Euler-equation and the consumption function are considered, providing insight into the consequences and side effects of naiveté. The purpose of this paper is the analysis of how parameters of the discounting function influence the risk-free rate and asset distributions. It is found that the level of naiveté plays a particularly important part in determining interest rates – high levels of it imply high interest rates. The other main result is that there might be large inequalities in heterogeneous populations (where heterogeneity is in the hyperbolic discount factor and the level of naiveté). This thesis shows that it also has significant welfare consequences – especially when the heterogeneity is in naiveté. This might be an important area of research in the future for policy analysis.
@mastersthesis{stancsics2016interest, title = {Interest Rates and Asset Distributions of Naive Hyperbolic Discounters}, author = {Stancsics, Martin}, year = {2016}, school = {Central European University}, }
2015
-
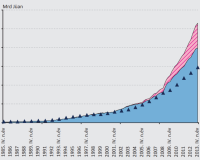 Kı́na: a tervgazdaságtól a modern bankrendszerigLaura Komlóssy, Zsolt Kovalszky, Gyöngyi Körmendi, and 2 more authorsFinancial and Economic Review 2015
Kı́na: a tervgazdaságtól a modern bankrendszerigLaura Komlóssy, Zsolt Kovalszky, Gyöngyi Körmendi, and 2 more authorsFinancial and Economic Review 2015Az elmúlt évtizedekben a gazdasági növekedés ütemét meghaladva, rendkívül gyors ütemben növekedett Kínában a banki aktivitás, melynek eredményeként mára nemzetközi léptékekben is óriási bankok alakultak ki. Az erõs állami kontroll ellenére a kínai bankok az utóbbi évtizedekben egyre inkább nyitottak a kereskedelem és a nemzetközi pénzpiacok felé, a szabályozói környezet rendellenességei miatt azonban az árnyékbankrendszer elterjedése a jelenlegi kínai pénzügyi rendszer egyik legnagyobb kockázati tényezõjévé vált, és elõretekintve érdemi instabilitást jelenthet. Az elmúlt pár évben a kínai növekedés egyre kiegyensúlyozatlanabbá vált, melyben hatalmas szerepe volt a bankrendszernek. A fogyasztás rendkívül alacsony GDP-részesedése mellett a beruházások példátlanul magas aránya felveti annak a kockázatát, hogy a beruházások túlzott mértékûek és fölösleges extra kapacitás kiépüléséhez járulnak hozzá, melyek végül hosszú távon nem vezetnek fenntartható növekedéshez, és a beruházások nem térülnek meg. A beruházások felfutásával párhuzamosan a hitelek állománya is növekedett, aminek tekintélyes része nem a hagyományos bankrendszerben ment végbe, így a fenti folyamatok könnyen nemteljesítõ adósságok felhalmozódásához és pénzügyi pánikhoz is vezethetnek, ami a gazdasági növekedés hirtelen lassulásával járna.
@article{laura2015kina, title = {K{\'\i}na: a tervgazdas{\'a}gt{\'o}l a modern bankrendszerig}, author = {Koml{\'o}ssy, Laura and Kovalszky, Zsolt and K{\"o}rmendi, Gy{\"o}ngyi and Lang, P{\'e}ter and Stancsics, Martin}, journal = {Financial and Economic Review}, volume = {14}, number = {5}, pages = {133--144}, year = {2015}, publisher = {Magyar Nemzeti Bank (Central Bank of Hungary)}, }
2014
-
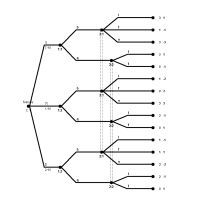 Az egyensúly vélekedés-alapú finomı́tásai szignáljátékokbanMartin Stancsics2014
Az egyensúly vélekedés-alapú finomı́tásai szignáljátékokbanMartin Stancsics2014A morális kockázatot leíró megbízó-ügynök modelleknél különféle feltevésekkel szoktunk élni, melyek közül néhány plauzibilis, néhány pedig kevésbé. Az egyik általános feltevés az, hogy az ügynök hasznosságfüggvénye kétszer differenciálható, illetve bérben és erőfeszítésben szétválasztható. Ez nagyban megkönnyíti a számolást, azonban vannak olyan helyzetek, ahol egyszerűen nem reális. Fehr és Gotte (2007) egy kerékpáros futárokat vizsgáló kísérlet alapján arra jutott, hogy a futárok által kifejtett erőfeszítést nem magyarázza meg a hagyományos szétválasztható neoklasszikus hasznosságfüggvény. Az egyik modell, amit javasoltak helyette, egy viselkedési közgazdaságtanon alapuló modell volt, amelyben a futároknak volt egy kitűzött jövedelemcélja, amelyet mindenképpen el szerettek volna érni, és miután azt elérték, csökkent számukra a pénz határhaszna. Hasznosságfüggvényük nem volt mindenhol differenciálható a bér szerint. Dolgozatomban arra keresem a választ, hogy ilyen típusú ügynököket tartalmazó, morális kockázattal jellemezhető helyzetekben hogyan lehet megkeresni az egyensúlyi pontot, milyen szerződést ajánl a megbízó, illetve milyen plusz feltevésekkel kell élnünk, hogy viszonylag egyszerűen eredményhez jussunk. A dolgozat első felében bemutatom, miben változik az optimumfeladat, amennyiben az ügynök hasznosságfüggvénye legfeljebb megszámlálható sok helyen nem differenciálható. Ezután felírom ennek egy speciális esetét, egy egyszerűsített modellt, amin keresztül megvizsgálom az egyensúly tulajdonságait ilyen feltételek mellett.
@bachelorsthesis{stancsics2014az, title = {Az egyens{\'u}ly v{\'e}leked{\'e}s-alap{\'u} finom{\'\i}t{\'a}sai szign{\'a}lj{\'a}t{\'e}kokban}, author = {Stancsics, Martin}, year = {2014}, school = {BCE K{\"o}zgazdas{\'a}gtudom{\'a}nyi Kar}, }